Geometry pack: Where do we see geometry in Islam?

Use these six activities to explore the geometry found in Islamic design with students in KS2.
The six activities in this pack have been developed to explore with students the intricate geometry that is found in Islamic design, particularly on tiles, carpets and pottery, and in architecture. They are linked to the Year 6 enquiry of learning Where do we find beauty in Nature?, through which children can explore the principle of Health. They can be used to support learning about shape, tessellation and rotational symmetry in maths, as a stimulus for learning in art or to teach geometry as a standalone activity. They could also be used to introduce students to the principle of Geometry.
For each activity, step-by-step instructions are provided as a guide for teachers, with accompanying diagrams and lists of the resources students will need to complete each activity. There are also photocopiable templates to help students complete each activity.
You can download the whole pack via the download button at the bottom of this page.
We recommend the use of Jakar compasses for geometric drawing, which are easier for children to use accurately. They can be purchased at a discounted rate here on our website.
What’s in this geometry teaching pack?
The following six activities are included in this pack:
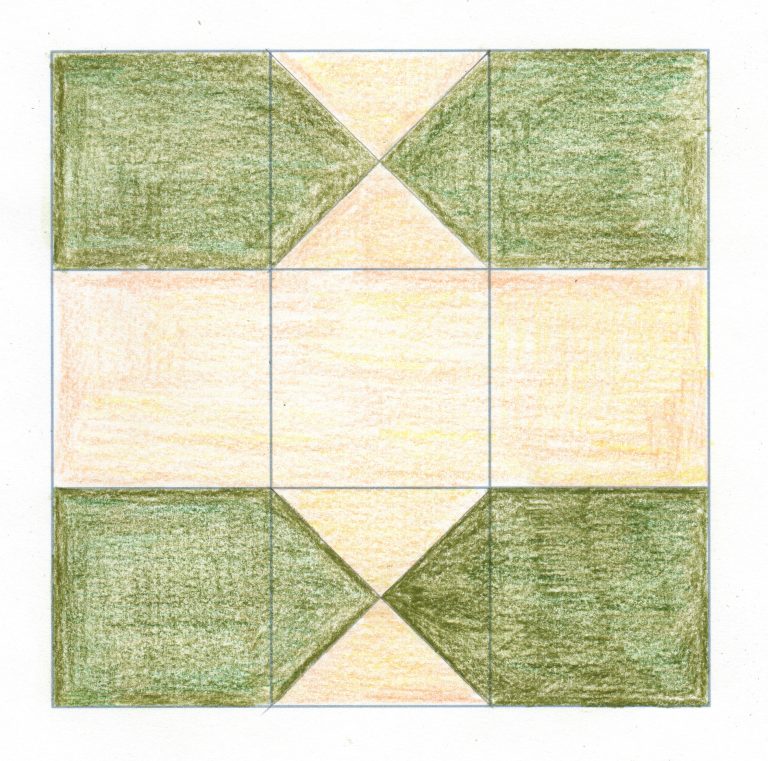
How can I draw an Islamic pattern using a grid?
In this activity, students use a square grid template to create a tessellating tile design. This can be duplicated and used to build up a more detailed design for wall or floor decoration. To take the activity further, students can add additional embellishment, using images of Islamic tiles for inspiration.
Many of the tiled patterns found at the Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain are based on square grids like the one used in this activity and cover large areas of wall.
How can I draw an Islamic eight-pointed star?
Students use a compass in this activity to create their own template for a square tile design and explore the ways that circles and squares interact. A template is provided to adapt the activity for students requiring additional support, or if compasses are unavailable.
Each student’s finished tile can be displayed alongside others to create a visually impactful classroom display or collaborative class artwork.
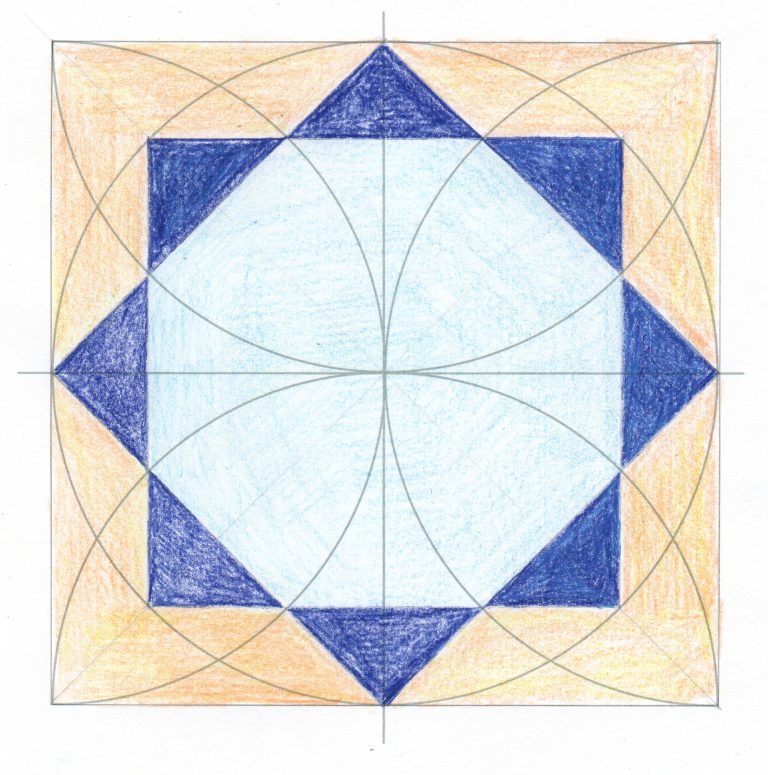
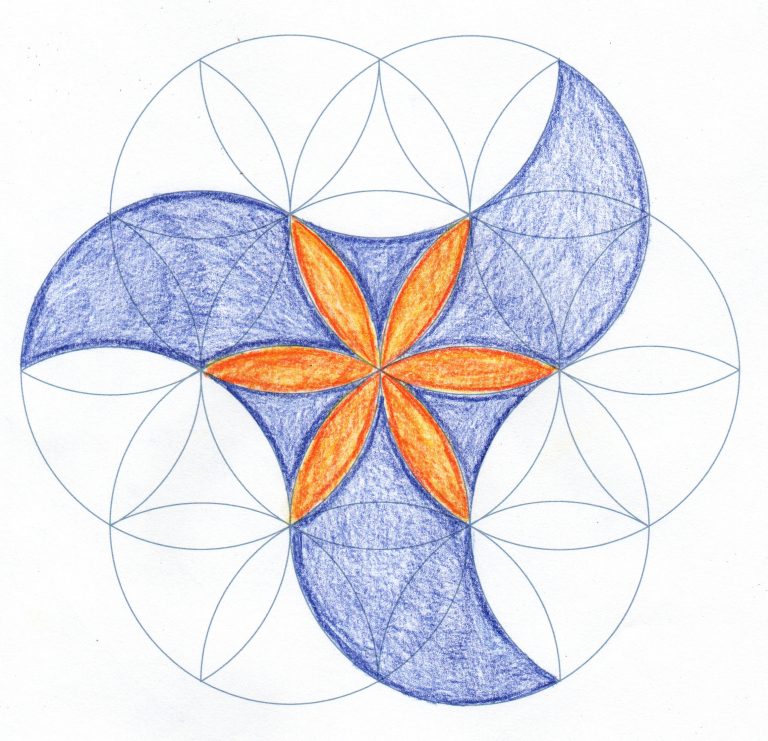
How can I draw an Islamic pattern from the Alhambra?
The renowned geometric tiles and surface decoration found in the Alhambra Palace in Granada, Spain are once again the inspiration for the third activity in this pack. Comprising stars, polygons and other symmetrical shapes, the beautifully intricate designs created by the architects and artists who worked on the palace represent the balance and order of our world.
Again, in this activity students use compasses to create a template for a design that is the perfect stimulus for exploring tessellation in maths or in art and design.
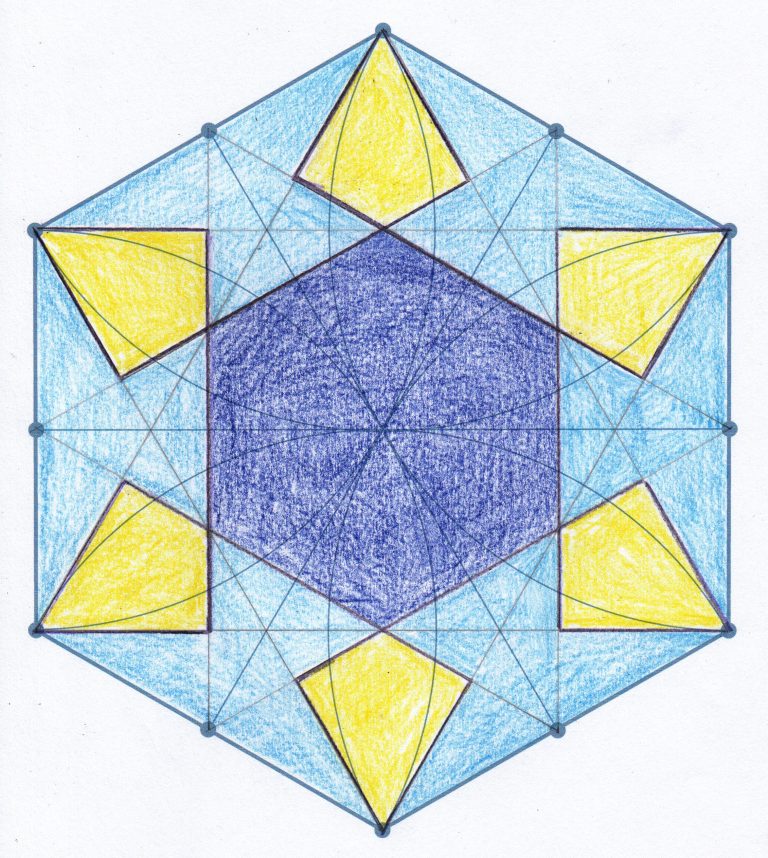
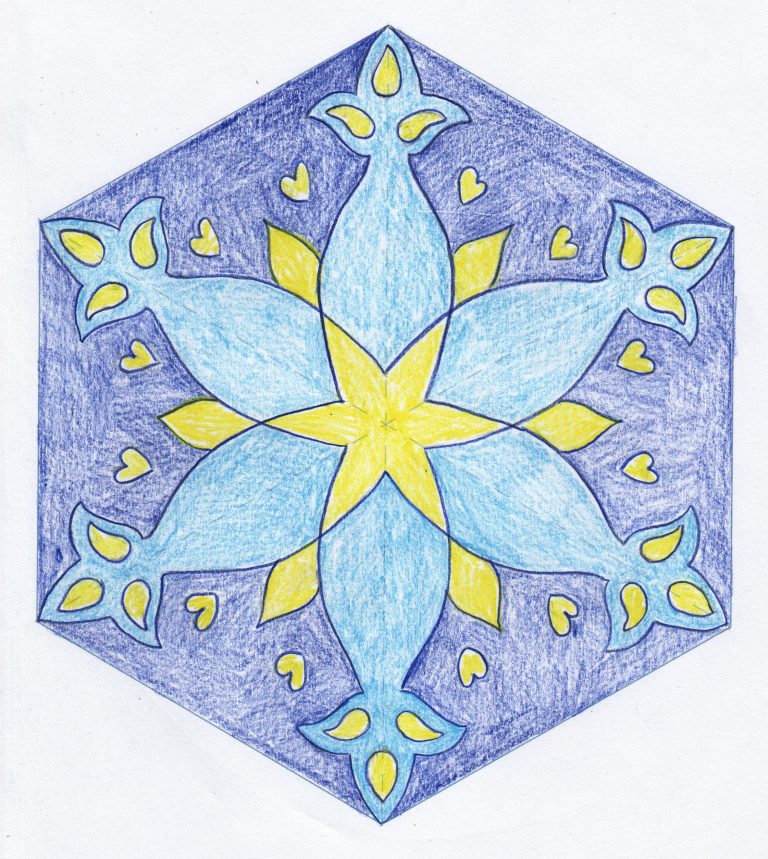
How can I develop a repeated pattern for a tile?
In this activity, students use rotational symmetry to design a hexagonal tile inspired by the geometric representations of flowers found in Islamic art. This can support learning about rotational symmetry in maths or learning in art.
The students’ completed hexagonal tile designs can be placed together in one large, striking class display. Alternatively, each student’s design can be duplicated and arranged to create an individual ’tiled’ surface decoration.

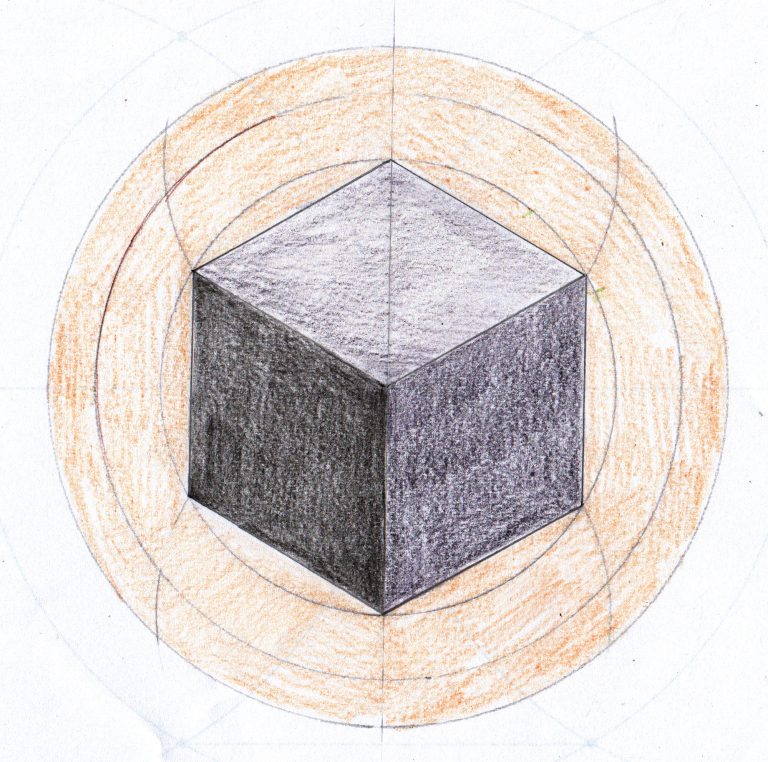
How can I represent the cube and circles of the Kaaba?
The fifth activity in this pack can be used to support learning about 3D shape in maths or as an introduction to 3D drawing techniques in art and design. Students use a compass to create a template that they then use to complete a 3D drawing of a cube.
This references the cubic form of the Kaaba, a holy site in the city of Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Every year, millions of Muslims from all over the world visit the Kaaba, walking around it in a circle to show their love and devotion to God.
How can I use tessellation to create a geometric pattern?
In the final activity in this pack, students explore the use of tessellation in geometric Islamic designs that feature repeating shapes such as hexagons and kites.
When these shapes are arranged next to each other with sides touching, other shapes often emerge, create a flowing pattern that can cover an entire wall.